Anita Bryant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Anita Jane Bryant (born March 25, 1940) is an American singer known for anti-gay activism. She scored four "Top 40" hits in the United States in the late 1950s and early 1960s, including "
 In 1960, Bryant married Bob Green (1931–2012), a Miami disc jockey, with whom she eventually raised four children: Robert Jr. (Bobby), Gloria, and twins Billy and Barbara. She divorced him in 1980, attracting allegations of hypocrisy from the
In 1960, Bryant married Bob Green (1931–2012), a Miami disc jockey, with whom she eventually raised four children: Robert Jr. (Bobby), Gloria, and twins Billy and Barbara. She divorced him in 1980, attracting allegations of hypocrisy from the 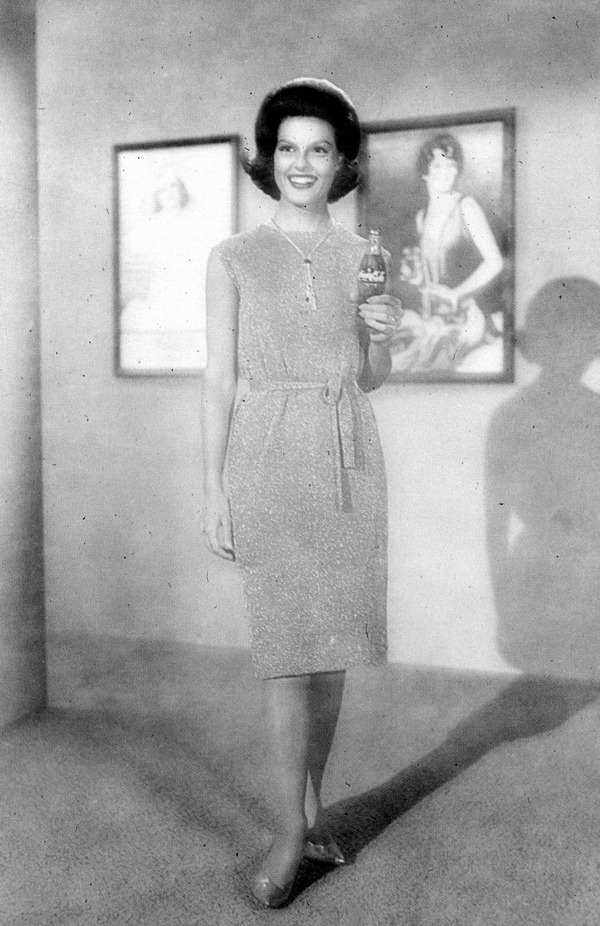 Bryant released several albums on the
Bryant released several albums on the
 In 1977,
In 1977,
 On June 7, 1977, Bryant's campaign led to a repeal of the anti-discrimination ordinance by a margin of 69 to 31 percent. However, the success of Bryant's campaign galvanized her opponents, and the gay community retaliated against her by forming the Coalition for Human Rights and the Miami Victory Campaign, who organized a boycott of orange juice.
On June 7, 1977, Bryant's campaign led to a repeal of the anti-discrimination ordinance by a margin of 69 to 31 percent. However, the success of Bryant's campaign galvanized her opponents, and the gay community retaliated against her by forming the Coalition for Human Rights and the Miami Victory Campaign, who organized a boycott of orange juice.
Anita Bryant Ministries International
*
Image of Anita Bryant in the 1970s
(Available for public use from the
Belated curtain call
''Tulsa World'', April 19, 2007
Readers Forum: Anita Bryant to star in Round-Up 2007
''Tulsa World'', April 18, 2007
Celebration draws Anita Bryant back to Barnsdall
''Tulsa World'', May 28, 2005
''
Paper Roses
"Paper Roses" is a popular song written and composed by Fred Spielman and Janice Torre. It first was a top five hit in 1960 for Anita Bryant. Marie Osmond recorded it in 1973 and took her version to number one on the US country chart.
Anit ...
" which reached No. 5 on the charts. She was the 1958 Miss Oklahoma
The Miss Oklahoma competition selects a winner to compete on behalf of Oklahoma in the Miss America pageant. Miss Oklahoma has won the Miss America crown on five occasions. Also, in the years when city representatives were common, Norma Smallw ...
beauty pageant winner, and a brand ambassador from 1969 to 1980 for the Florida Citrus Commission.
In the 1970s, Bryant became known as an outspoken opponent of gay rights
Rights affecting lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people vary greatly by country or jurisdiction—encompassing everything from the legal recognition of same-sex marriage to the death penalty for homosexuality.
Notably, , 3 ...
in the U.S. In 1977, she ran the "Save Our Children
Save Our Children, Inc. was an American political coalition formed in 1977 in Miami, Florida, to overturn a recently legislated county ordinance that banned discrimination in areas of housing, employment, and public accommodation based on sexua ...
" campaign to repeal a local ordinance in Miami-Dade County, Florida
Miami-Dade County is a County (United States), county located in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Florida. The county had a population of 2,701,767 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it the most populous county in ...
, that prohibited discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation. Her involvement with the campaign was condemned by gay rights activists. They were assisted by many other prominent figures in music, film, and television, and retaliated by boycotting the orange juice that she promoted. Though the campaign ended successfully with a 69% majority vote to repeal the ordinance on June 7, 1977 (Dade County restored the ordinance in 1998), it permanently damaged her public image, and her contract with the Florida Citrus Commission was terminated three years later. This, as well as her later divorce from Bob Green, damaged her financially. Bryant never regained her former prominence and filed for bankruptcy twice. She lives in her home state of Oklahoma.
Early life and career
Bryant was born inBarnsdall, Oklahoma {{Infobox settlement
, official_name = Barnsdall, Oklahoma
, settlement_type = City
, nickname = Bigheart
, motto =
, image_caption =
, image_flag =
, image_se ...
, the daughter of Lenora A. (Berry) and Warren Bryant. After her parents divorced, her father went into the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
and her mother went to work as a clerk for Tinker Air Force Base
Tinker Air Force Base is a major United States Air Force base, with tenant U.S. Navy and other Department of Defense missions, located in Oklahoma County, Oklahoma, surrounded by Del City, Oklahoma City, and Midwest City.
The base, origina ...
, taking her children to live with their grandparents temporarily. When Bryant was two years old, her grandfather taught her to sing "Jesus Loves Me
"Jesus Loves Me" is a Christian hymn written by Anna Bartlett Warner (1827–1915). The lyrics first appeared as a poem in the context of an 1860 novel called ''Say and Seal'', written by her older sister Susan Warner (1819–1885), in which t ...
". She was singing onstage at the age of six, at local fairgrounds in Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
. She sang occasionally on radio and television, and was invited to audition when Arthur Godfrey
Arthur Morton Godfrey (August 31, 1903 – March 16, 1983) was an American radio and television broadcaster and entertainer who was sometimes introduced by his nickname The Old Redhead. At the peak of his success, in the early-to-mid 1950s, Godf ...
's talent show came to town.
Bryant became Miss Oklahoma in 1958, and was second runner-up in the 1959 Miss America
Miss America is an annual competition that is open to women from the United States between the ages of 17 and 25. Originating in 1921 as a "bathing beauty revue", the contest is now judged on competitors' talent performances and interviews. As ...
pageant
Pageant may refer to:
* Procession or ceremony in elaborate costume
* Beauty pageant, or beauty contest
* Latter Day Saint plays and pageants, run by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints or by members local to the area of the pageant
* ...
(held September 6, 1958) at age 18, right after graduating from Tulsa's Will Rogers High School
Will Rogers Middle and High School, located at 3909 E. 5th Place in Tulsa, Oklahoma, was built by Tulsa Public Schools in 1939 using WPA workers and designed by Joseph R. Koberling, Jr. and Leon B. Senter. It was named for the humorist Will Rog ...
.
Christian right
The Christian right, or the religious right, are Christian political factions characterized by their strong support of socially conservative and traditionalist policies. Christian conservatives seek to influence politics and public policy with t ...
, who cited the indissolubility of Christian marriage
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρισ ...
which Bryant had championed, and "the deterioration of the family" against which she had preached. She appeared early in her career on the NBC
The National Broadcasting Company (NBC) is an American English-language commercial broadcast television and radio network. The flagship property of the NBC Entertainment division of NBCUniversal, a division of Comcast, its headquarters are l ...
interview program ''Here's Hollywood
''Here's Hollywood'' is an American celebrity interview program which aired on weekday afternoons on NBC at 4:30 Eastern time from September 26, 1960, to December 28, 1962.
Overview
In the first season, the interviews were conducted by Dean Mill ...
'' and on the same network's ''The Ford Show
''The Ford Show'' (also known as ''The Ford Show, Starring Tennessee Ernie Ford'' and ''The Tennessee Ernie Ford Show'') is an American variety program, starring singer and folk humorist Tennessee Ernie Ford, which aired on NBC on Thursday eveni ...
'', starring Tennessee Ernie Ford
Ernest Jennings Ford (February 13, 1919 – October 17, 1991), known professionally as Tennessee Ernie Ford, was an American singer and television host who enjoyed success in the country and western, pop, and gospel musical genres. Noted for h ...
.
Between 1964 and 1969, Bryant performed at multiple White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. ...
functions, including both the Democratic Convention
The Democratic National Convention (DNC) is a series of presidential nominating conventions held every four years since 1832 by the United States Democratic Party. They have been administered by the Democratic National Committee since the 1852 ...
in Chicago and the Miami Republican Convention
The Republican National Convention (RNC) is a series of U.S. presidential nominating convention, presidential nominating conventions held every four years since 1856 by the United States Republican Party. They are administered by the Republican N ...
in 1968.
From 1961 until 1968, Bryant frequently joined Bob Hope
Leslie Townes "Bob" Hope (May 29, 1903 – July 27, 2003) was a British-American comedian, vaudevillian, actor, singer and dancer. With a career that spanned nearly 80 years, Hope appeared in Bob Hope filmography, more than 70 short and ...
on holiday tours for the United Service Organizations
The United Service Organizations Inc. (USO) is an American nonprofit-charitable corporation that provides live entertainment, such as comedians, actors and musicians, social facilities, and other programs to members of the United States Armed F ...
. She again traveled with Hope for televised shows during the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
. Bryant was given the Silver Medallion Award from the National Guard
National Guard is the name used by a wide variety of current and historical uniformed organizations in different countries. The original National Guard was formed during the French Revolution around a cadre of defectors from the French Guards.
Nat ...
for "outstanding service by an entertainer", and the Veterans of Foreign Wars Leadership Gold Medallion.
Bryant had a total of 11 songs on the U.S. Hot 100. She had a moderate pop hit with "Till There Was You
"Till There Was You" is a show tune written in 1950 by Meredith Willson, originally entitled "Till I Met You." It was originally recorded October 25, 1950, by Meredith Willson & his Orchestra and Eileen Wilson. The song was retitled and used ...
" (1959, US No. 30), from the Broadway production ''The Music Man
''The Music Man'' is a musical with book, music, and lyrics by Meredith Willson, based on a story by Willson and Franklin Lacey. The plot concerns con man Harold Hill, who poses as a boys' band organizer and leader and sells band instruments ...
''. She also had three hits in "Paper Roses
"Paper Roses" is a popular song written and composed by Fred Spielman and Janice Torre. It first was a top five hit in 1960 for Anita Bryant. Marie Osmond recorded it in 1973 and took her version to number one on the US country chart.
Anit ...
" (1960, US No. 5, and covered by Marie Osmond
Olive Marie Osmond (born October 13, 1959) is an American singer, actress, television host, and a member of the show business family the Osmonds. Although she was never part of her family's singing group, she gained success as a country and pop ...
13 years later), "In My Little Corner of the World
''In My Little Corner of the World'' is the second studio album by American country music singer Marie Osmond. It was released on MGM Records in 1974.
Marie Osmond's second album was named after the lead and only single from the album, " In My ...
" (1960, US No. 10), and "Wonderland by Night
"Wonderland by Night" (German title ''"Wunderland bei Nacht"'') is a popular song by Bert Kaempfert that was a '' Billboard'' number one hit for three weeks, starting January 9, 1961. It was recorded in July 1959. The song was written by Klaus G ...
" (1961, US No. 18), originally a hit for Bert Kaempfert
Bert Kaempfert (born Berthold Heinrich Kämpfert; 16 October 1923 – 21 June 1980) was a German orchestra leader, multi-instrumentalist, music producer, arranger, and composer. He made easy listening and jazz-oriented records and wrote the mus ...
. "Paper Roses", "In My Little Corner of the World", and "Till There Was You", each sold over one million copies, and were awarded a gold disc
Music recording certification is a system of certifying that a music recording has shipped, sold, or streamed a certain number of units. The threshold quantity varies by type (such as album, single, music video) and by nation or territory (see ...
by the RIAA
The Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA) is a trade organization that represents the music recording industry in the United States. Its members consist of record labels and distributors that the RIAA says "create, manufacture, and/o ...
.
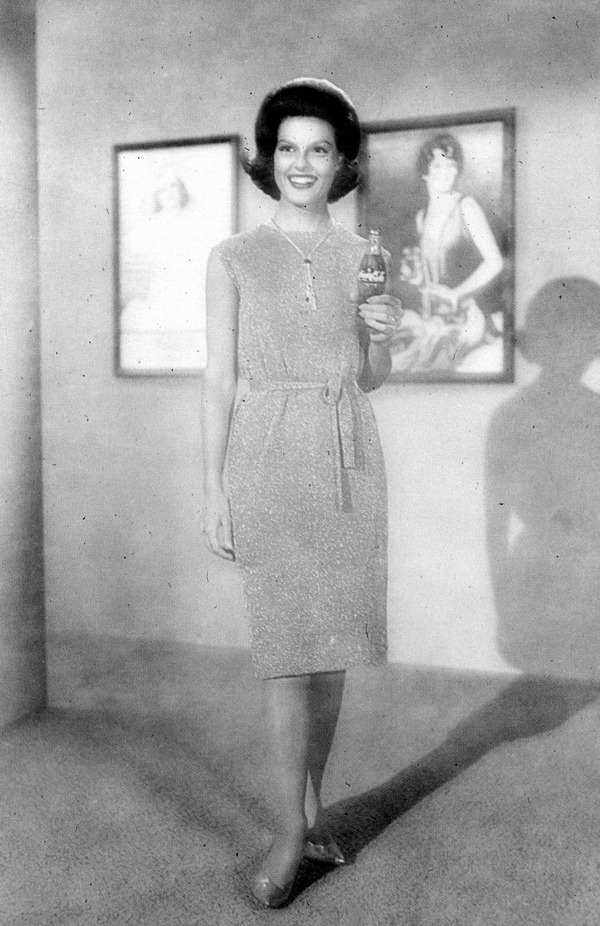 Bryant released several albums on the
Bryant released several albums on the Carlton
Carlton may refer to:
People
* Carlton (name), a list of those with the given name or surname
* Carlton (singer), English soul singer Carlton McCarthy
* Carlton, a pen name used by Joseph Caldwell (1773–1835), American educator, Presbyterian ...
and Columbia labels. Her first album, eponymously titled and released in 1959, contained "Till There Was You" and other songs from other Broadway shows. Her second album, ''Hear Anita Bryant in Your Home Tonight'' (1961), contains "Paper Roses" and "Wonderland by Night", as well as several songs that first appeared in her singles. Her third album, ''In My Little Corner of the World'', also in 1961, contains the title song and other songs that have to do with places around the world, including "Canadian Sunset" and "I Love Paris". Bryant's compilation album, ''Greatest Hits'' (1963), contains both her original Carlton hits (because Columbia purchased all the masters from Carlton) plus sides from her Columbia recordings, including "Paper Roses" and "Step by Step, Little by Little". In 1964, she released ''The World of Lonely People'', containing, in addition to the title song, "Welcome, Welcome Home" and a new rendition of "Little Things Mean a Lot", arranged by Frank Hunter. Bryant also released several albums of religious music.
In 1969, Bryant became a spokeswoman for the Florida Citrus Commission, and nationally televised commercials featured her singing "Come to the Florida Sunshine Tree" and stating the commercials' tagline: "Breakfast without orange juice is like a day without sunshine." (Later, the slogan became, "It isn't just for breakfast anymore!") In addition during that time, she appeared in advertisements for Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola, or Coke, is a carbonated soft drink manufactured by the Coca-Cola Company. Originally marketed as a temperance drink and intended as a patent medicine, it was invented in the late 19th century by John Stith Pemberton in Atlanta ...
, Kraft Foods
The second incarnation of Kraft Foods is an American food manufacturing and processing conglomerate, split from Kraft Foods Inc. in 2012 and headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. It became part of Kraft Heinz in 2015.
A merger with Heinz, arra ...
, Holiday Inn
Holiday Inn is an American chain of hotels based in Atlanta, Georgia. and a brand of IHG Hotels & Resorts. The chain was founded in 1952 by Kemmons Wilson, who opened the first location in Memphis, Tennessee that year. The chain was a division ...
, and Tupperware
Tupperware is an American home products line that includes preparation, storage, and serving products for the kitchen and home. In 1942, Earl Tupper developed his first bell-shaped container; the brand products were introduced to the public in 1 ...
. In the 1970s, Bryant was teamed up with the Disney Character " Orange Bird", with whom she appeared in several orange juice commercials. She also sang the Orange Bird Song and narrated the Orange Bird record album, with music written by the Sherman Brothers. She also published her cookbook, Bless This Food: The Anita Bryant Family Cookbook, described as "Much more than a cookbook, this is the story of a family devoted to Christ."
Bryant sang "The Battle Hymn of the Republic
The "Battle Hymn of the Republic", also known as "Mine Eyes Have Seen the Glory" or "Glory, Glory Hallelujah" outside of the United States, is a popular American patriotic song written by the abolitionist writer Julia Ward Howe.
Howe wrote her l ...
" during the half-time show of Super Bowl V
Super Bowl V was an American football game played between the American Football Conference (AFC) champion Baltimore Colts and the National Football Conference (NFC) champion Dallas Cowboys to determine the National Football League (NFL) champio ...
in 1971, and at the graveside services for President of the United States Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
in 1973.
Bryant hosted a two-hour television special, ''The Anita Bryant Spectacular'', in March 1980. She recounted her autobiography, appeared in medleys of prerecorded songs, and interviewed Pat Boone
Patrick Charles Eugene Boone (born June 1, 1934) is an American singer and actor. He was a successful pop singer in the United States during the 1950s and early 1960s. He sold more than 45 million records, had 38 Top 40 hits, and appeared in mo ...
. The West Point
The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known Metonymy, metonymically as West Point or simply as Army, is a United States service academies, United States service academy in West Point, New York. It was originally established as a f ...
Glee Club
A glee club in the United States is a musical group or choir group, historically of male voices but also of female or mixed voices, which traditionally specializes in the singing of short songs by trios or quartets. In the late 19th century it w ...
and General William Westmoreland
William Childs Westmoreland (March 26, 1914 – July 18, 2005) was a United States Army general, most notably commander of United States forces during the Vietnam War from 1964 to 1968. He served as Chief of Staff of the United States Army from ...
participated.
Anti-gay rights activism
Bryant is known for her anti-gay rights activism. On March 23, 1969, Bryant participated in a ''Rally for Decency'' at theOrange Bowl
The Orange Bowl is an annual American college football bowl game played in the Miami metropolitan area. It has been played annually since January 1, 1935, making it, along with the Sugar Bowl and the Sun Bowl, the second-oldest bowl game ...
to protest an incident involving Jim Morrison
James Douglas Morrison (December 8, 1943 – July 3, 1971) was an American singer, poet and songwriter who was the lead vocalist of the Rock music, rock band the Doors. Due to his wild personality, poetic lyrics, distinctive voice, unpredicta ...
and The Doors
The Doors were an American Rock music, rock band formed in Los Angeles in 1965, with vocalist Jim Morrison, keyboardist Ray Manzarek, guitarist Robby Krieger, and drummer John Densmore. They were among the most controversial and influential ro ...
' performance in Miami, Florida in 1969.
 In 1977,
In 1977, Dade County, Florida
Miami-Dade County is a county located in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Florida. The county had a population of 2,701,767 as of the 2020 census, making it the most populous county in Florida and the seventh-most populous county in ...
, passed an ordinance
Ordinance may refer to:
Law
* Ordinance (Belgium), a law adopted by the Brussels Parliament or the Common Community Commission
* Ordinance (India), a temporary law promulgated by the President of India on recommendation of the Union Cabinet
* ...
sponsored by Bryant's former friend Ruth Shack
Ruth Shack (born August 24, 1931) is an American politician who served as the sponsor of the 1977 Human Rights Ordinance in Miami-Dade County, Florida. She was elected to the Metro-Dade County Commission in 1976, 1978 and 1982. After leaving the ...
that prohibited discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation
Sexual orientation is an enduring pattern of romantic or sexual attraction (or a combination of these) to persons of the opposite sex or gender, the same sex or gender, or to both sexes or more than one gender. These attractions are generall ...
. Bryant led a highly publicized campaign to repeal the ordinance, as the leader of a coalition named Save Our Children
Save Our Children, Inc. was an American political coalition formed in 1977 in Miami, Florida, to overturn a recently legislated county ordinance that banned discrimination in areas of housing, employment, and public accommodation based on sexua ...
. The campaign was based on conservative Christian beliefs regarding the sinfulness of homosexuality and the proposed threat of homosexual recruitment of children and child molestation. Bryant stated:
She also perpetuated idea of the gay community 'recruiting' children through child abuse to become homosexual themselves. When Shack and other leaders refused to vote in opposition to the ordinance as per her request, she started promoting fear in the press to get families on her side. She stated in the news, ""The recruitment of our children is absolutely necessary for the survival and growth of homosexuality… for since homosexuals cannot reproduce, they must recruit, must freshen their ranks."
The campaign marked the beginning of an organized opposition to gay rights that spread across the nation. Jerry Falwell Sr.
Jerry Laymon Falwell Sr. (August 11, 1933 – May 15, 2007) was an American Baptist pastor, televangelism, televangelist, and conservatism in the United States, conservative activist. He was the founding pastor of the Thomas Road Baptist Church, ...
went to Miami to help Bryant. She made the following statements during the campaign: "As a mother, I know that homosexuals cannot biologically reproduce children; therefore, they must recruit our children" and "If gays are granted rights, next we'll have to give rights to prostitutes and to people who sleep with St. Bernards and to nail biters." She also said, "All America and all the world will hear what the people have said, and with God's continued help we will prevail in our fight to repeal similar laws throughout the nation." Notably, Bryant referred to gay people as "human garbage".
The name of the campaign had to be changed to "Protect America's Children" because of legal action by the Save the Children
The Save the Children Fund, commonly known as Save the Children, is an international non-governmental organization established in the United Kingdom in 1919 to improve the lives of children through better education, health care, and economic ...
foundation.
Victory and defeat
 On June 7, 1977, Bryant's campaign led to a repeal of the anti-discrimination ordinance by a margin of 69 to 31 percent. However, the success of Bryant's campaign galvanized her opponents, and the gay community retaliated against her by forming the Coalition for Human Rights and the Miami Victory Campaign, who organized a boycott of orange juice.
On June 7, 1977, Bryant's campaign led to a repeal of the anti-discrimination ordinance by a margin of 69 to 31 percent. However, the success of Bryant's campaign galvanized her opponents, and the gay community retaliated against her by forming the Coalition for Human Rights and the Miami Victory Campaign, who organized a boycott of orange juice. Gay bar
A gay bar is a drinking establishment that caters to an exclusively or predominantly lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) clientele; the term ''gay'' is used as a broadly inclusive concept for LGBT communities.
Gay bars once served as ...
s all over North America stopped serving screwdrivers
A screwdriver is a tool, manual or powered, used for turning screws. A typical simple screwdriver has a handle and a shaft, ending in a tip the user puts into the screw head before turning the handle. This form of the screwdriver has been repla ...
and replaced them with the "Anita Bryant Cocktail", which was made with vodka
Vodka ( pl, wódka , russian: водка , sv, vodka ) is a clear distilled alcoholic beverage. Different varieties originated in Poland, Russia, and Sweden. Vodka is composed mainly of water and ethanol but sometimes with traces of impuritie ...
and apple juice. Also merchandise such as buttons, bumper stickers, and t-shirts with slogans such as "A day without human rights is like a day without sunshine" were sold to push the anti-discrimination movement further. Sales and proceeds went to gay rights activists to help fund their fight against Bryant and her campaign.
In 1977, Florida legislators approved a measure prohibiting gay adoption
Same-sex adoption is the adoption of children by same-sex couples. It may take the form of a joint adoption by the couple, or of the adoption by one partner of the other's biological child ( stepchild adoption).
Joint adoption by same-sex co ...
. The ban was overturned more than 30 years later when, on November 25, 2008, Miami-Dade Circuit Court Judge Cindy S. Lederman declared it unconstitutional.
Bryant became one of the first persons to be publicly "pied
A piebald or pied animal is one that has a pattern of unpigmented spots (white) on a pigmented background of hair, feathers or scales. Thus a piebald black and white dog is a black dog with white spots. The animal's skin under the white backgro ...
" as a political act. During a television appearance in Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the ...
on October 14, 1977, Bryant was struck by a pie thrown at her by Thom L. Higgins (1950–1994). Bryant quipped "At least it's a fruit pie," making a pun on the derogatory slur of "fruit" for a gay man. While covered in pie, she began to pray to God to forgive the activist "for his deviant lifestyle" before bursting into tears as the cameras continued rolling. Bryant's husband said that he would not retaliate, but followed the protesters outside and threw a pie at them. By this time, gay activists ensured that the boycott on Florida orange juice had become more prominent and it was supported by many celebrities, including Paul Williams, Vincent Price
Vincent Leonard Price Jr. (May 27, 1911 – October 25, 1993) was an American actor, art historian, art collector and gourmet cook. He appeared on stage, television, and radio, and in more than 100 films. Price has two stars on the Hollywood Wal ...
(he joked in a television interview that Oscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish poet and playwright. After writing in different forms throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular playwrights in London in the early 1890s. He is ...
's ''A Woman of No Importance
''A Woman of No Importance'' by Oscar Wilde is "a new and original play of modern life", in four acts, first given on 19 April 1893 at the Haymarket Theatre, London. Like Wilde's other society plays, it satirises English upper-class society. It ...
'' referred to her), and Jane Fonda. Johnny Carson
John William Carson (October 23, 1925 – January 23, 2005) was an American television host, comedian, writer and producer. He is best known as the host of ''The Tonight Show Starring Johnny Carson'' (1962–1992). Carson received six Pr ...
also made Bryant a regular target of ridicule in his nightly monologues. In 1978, Bryant and Bob Green told the story of their campaign in the book ''At Any Cost''. The gay community continued to regard Bryant's name as synonymous with bigotry
Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of race, gender, age, rel ...
and homophobia
Homophobia encompasses a range of negative attitude (psychology), attitudes and feelings toward homosexuality or people who are identified or perceived as being lesbian, gay or bisexual. It has been defined as contempt, prejudice, aversion, h ...
. But at the same time, her name became a call to action for gay rights activists, and motivated many to picket her events, host anti-Bryant protests across the country, and increase attendance and frequency of pride marches.
Bryant led several more campaigns around the country to repeal local anti-discrimination ordinances, including campaigns in St. Paul, Minnesota; Wichita, Kansas
Wichita ( ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Kansas and the county seat of Sedgwick County, Kansas, Sedgwick County. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population of the city was 397,532. The Wichita metro area had ...
; and Eugene, Oregon
Eugene ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Oregon. It is located at the southern end of the Willamette Valley, near the confluence of the McKenzie and Willamette rivers, about east of the Oregon Coast.
As of the 2020 United States Census, Eu ...
. In 1978, her success led to the Briggs Initiative
California Proposition 6, informally known as the Briggs Initiative, was a ballot initiative put to a referendum on the California state ballot in the November 7, 1978 election. It was sponsored by John Briggs, a conservative state legislator ...
in California, which would have made pro-gay statements regarding homosexual people or homosexuality by any public school
Public school may refer to:
* State school (known as a public school in many countries), a no-fee school, publicly funded and operated by the government
* Public school (United Kingdom), certain elite fee-charging independent schools in England an ...
employee cause for dismissal. Grassroots liberal organizations, chiefly in Los Angeles and the San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, often referred to as simply the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. The Bay Area is defined by the Association of Bay Area Go ...
, organized to defeat the initiative. Days before the election, the California Democratic Party
The California Democratic Party is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in the U.S. state of California. It is headquartered in Sacramento.
With 43.5% of the state's registered voters as of 2018, the Democratic Party has the highest number of r ...
opposed the proposed legislation. President Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he previously served as th ...
, Governor Jerry Brown
Edmund Gerald Brown Jr. (born April 7, 1938) is an American lawyer, author, and politician who served as the 34th and 39th governor of California from 1975 to 1983 and 2011 to 2019. A member of the Democratic Party, he was elected Secretary of S ...
, former president Gerald Ford
Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. ( ; born Leslie Lynch King Jr.; July 14, 1913December 26, 2006) was an American politician who served as the 38th president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He was the only president never to have been elected ...
, and former governor Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
—then planning a run for the presidency—all voiced opposition to the initiative, and it ultimately suffered a massive defeat at the polls.
In 1998, the Miami-Dade County Commission narrowly reinstated the ordinance protecting individuals from discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation, by a narrow 7-6 vote. In 2002, a ballot initiative to repeal the 1998 law, called Amendment 14, was voted down by 56 percent of the voters. The Florida statute forbidding gay adoption was upheld in 2004 by a federal appellate court
A court of appeals, also called a court of appeal, appellate court, appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to hear an appeal of a trial court or other lower tribunal. In much of ...
against a constitutional challenge but was overturned by a Miami-Dade circuit court in November 2008.
In 2021, Bryant's granddaughter, Sarah Green, came out publicly by announcing her pending marriage to a woman, although she was having difficulty deciding whether she should invite her grandmother to the ceremony.
Career decline and bankruptcies
The fallout from Bryant's political activism hurt her business and entertainment career. In February 1977, theSinger Corporation
Singer Corporation is an American manufacturer of consumer sewing machines, first established as I. M. Singer & Co. in 1851 by Isaac M. Singer with New York lawyer Edward C. Clark. Best known for its sewing machines, it was renamed Singer Ma ...
rescinded an offer to sponsor an upcoming weekly variety show because of the "extensive national publicity arising from ryant'scontroversial political activities."
Bryant's marriage to Bob Green also failed at that time, and in 1980 she divorced him, citing emotional abuse and latent suicidal thoughts. Green refused to accept this, saying that his fundamentalist
Fundamentalism is a tendency among certain groups and individuals that is characterized by the application of a strict literal interpretation to scriptures, dogmas, or ideologies, along with a strong belief in the importance of distinguishi ...
religious beliefs did not recognize civil divorce and that she was still his wife "in God's eyes". In 2007, Green stated: "Blame gay people? I do. Their stated goal was to put her out of business and destroy her career. And that's what they did. It's unfair."
Some Christian fundamentalist
Christian fundamentalism, also known as fundamental Christianity or fundamentalist Christianity, is a religious movement emphasizing biblical literalism. In its modern form, it began in the late 19th and early 20th centuries among British and ...
audiences and venues shunned Bryant after her divorce. Because she was no longer invited to appear at their events, she lost a major source of income. The Florida Citrus Commission also allowed her contract to lapse after the divorce, stating that Bryant had "worn out" as a spokesperson.
Bryant rapidly became an object of ridicule, as her image shifted from being a model Christian spokeswoman to that of a self-righteous bigot. The decline of her reputation was aided by ''Tonight Show
''The Tonight Show'' is an American late-night talk show that has aired on NBC since 1954. The show has been hosted by six comedians: Steve Allen (1954–1957), Jack Paar (1957–1962), Johnny Carson (1962–1992), Jay Leno (1992–2009 and 2010� ...
'' host Johnny Carson, and other talk-show hosts and comedians, as they mocked her and her actions to the greater public. This led to many of her endorsements being cancelled and sponsors to drop her from their labels as she seemed to be a liability to them.
With three of her four children, she moved from Miami to Selma, Alabama, and later to Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,715 ...
, Georgia. In a 1980 '' Ladies' Home Journal'' article she said, "The church needs to wake up and find some way to cope with divorce and women's problems." She also expressed some sympathy for feminist aspirations, given her own experiences of emotional abuse within her previous marriage. Bryant also commented on her anti-gay views and said, "I'm more inclined to say live and let live, just don't flaunt it or try to legalize it." In a 2012 interview, her son Robert Green, Jr. said "she would be putting a lot more energy into fighting gay rights if she still felt as strongly."
Bryant appeared in Michael Moore
Michael Francis Moore (born April 23, 1954) is an American filmmaker, author and left-wing activist. His works frequently address the topics of globalization and capitalism.
Moore won the 2002 Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature for ' ...
's 1989 documentary film ''Roger & Me
''Roger & Me'' is a 1989 American documentary film written, produced, directed by, and starring Michael Moore, in his directorial debut. Moore portrays the regional economic impact of General Motors CEO Roger Smith's action of closing several ...
'', in which she is interviewed and travels to Flint, Michigan
Flint is the largest city and seat of Genesee County, Michigan, United States. Located along the Flint River, northwest of Detroit, it is a principal city within the region known as Mid Michigan. At the 2020 census, Flint had a population of 8 ...
, as part of the effort to revitalize its devastated local economy.
Bryant married her second husband, Charlie Hobson Dry, in 1990. The couple tried to reestablish her music career in a series of small venues, including Branson, Missouri
Branson is a city in the U.S. state of Missouri. Most of the city is situated in Taney County, with a small portion in the west extending into Stone County. Branson is in the Ozark Mountains. The community was named after Reuben Branson, postma ...
, and Pigeon Forge, Tennessee
Pigeon Forge is a mountain resort city in Sevier County, Tennessee, in the southeastern United States. As of the 2020 census, the city had a total population of 6,343. Situated just 5 miles (8 km) north of Great Smoky Mountains National Par ...
, where they opened ''Anita Bryant's Music Mansion''. The establishment combined Bryant's performances of her successful songs from early in her career with a "lengthy segment in which she preached her Christian beliefs". The venture was not successful and the Music Mansion, which had missed meeting payrolls at times, filed for bankruptcy in 2001 with Bryant and Dry leaving behind a series of unpaid employees and creditors.
Bryant also spent part of the 1990s in Branson, Missouri
Branson is a city in the U.S. state of Missouri. Most of the city is situated in Taney County, with a small portion in the west extending into Stone County. Branson is in the Ozark Mountains. The community was named after Reuben Branson, postma ...
, where the state and federal governments both filed liens claiming more than $116,000 in unpaid taxes. Bryant and Dry had also filed for Chapter 11
Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code (Title 11 of the United States Code) permits reorganization under the bankruptcy laws of the United States. Such reorganization, known as Chapter 11 bankruptcy, is available to every business, wheth ...
bankruptcy in Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
in 1997 after piling up bills from a failed Anita Bryant show in Eureka Springs
Eureka Springs is a city in Carroll County, Arkansas, United States, and one of two county seats for the county. It is located in the Ozark Mountains of northwest Arkansas, near the border with Missouri. As of the 2020 census, the city populat ...
, a tourist area in northwest Arkansas; among the debts were more than in unpaid state and federal taxes.
Other activities
In 2005, Bryant returned to Barnsdall, Oklahoma, to attend the town's 100th anniversary celebration and to have a street renamed in her honor. She returned to her high school in Tulsa on April 21, 2007, to perform in the school's annual musical revue. , she was living inEdmond, Oklahoma
Edmond is a city in Oklahoma County, Oklahoma, United States, and a part of the Oklahoma City metropolitan area in the central part of the state. The population was 94,428 according to the 2020 United States Census, making it the fifth largest cit ...
, and said she was doing charity work for various youth organizations while heading Anita Bryant Ministries International.
Writing
Mark D. Jordan
Mark D. Jordan (born 1953/54) is a scholar of Christian theology, European philosophy, and gender studies. He is currently the Richard Reinhard Niebuhr Research Professor of Divinity at Harvard Divinity School and Professor of the Studies of Women, ...
has written: "Many of her public statements, including her books, were ghostwritten by others, and there is internal reason to conclude that the most political books were pasted together by several hands from various sources."
*''Mine Eyes Have Seen the Glory'' (Old Tappan, NJ: Fleming H. Revell, 1970)
*''Amazing Grace'' (Old Tappan, NJ: Fleming H. Revell, 1971)
*''Bless This House'' (Old Tappan, NJ: Fleming H. Revell, 1972)
*''Bless This Food: The Anita Bryant Family Cookbook'' (NY: Doubleday, 1975)
*'' The Anita Bryant Story: The Survival of Our Nation's Families and the Threat of Militant Homosexuality'' (Old Tappan, NJ: Fleming H. Revell, 1977)
;With Bob Green
*''Fishers of Men'' (Old Tappan, NJ: Fleming H. Revell, 1973)
*''Light My Candle'' (Old Tappan, NJ: Fleming H. Revell, 1974)
*''Running the Good Race'' (Old Tappan, NJ: Fleming H. Revell, 1976), fitness guidance
*''Raising God's Children'' (Old Tappan, NJ: Fleming H. Revell, 1977)
Discography
Albums
Singles
In popular culture
Bryant's name has frequently been invoked as a prototypical example of opposition toLGBT rights
Rights affecting lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender ( LGBT) people vary greatly by country or jurisdiction—encompassing everything from the legal recognition of same-sex marriage to the death penalty for homosexuality.
Notably, ...
. When Elton John
Sir Elton Hercules John (born Reginald Kenneth Dwight; 25 March 1947) is a British singer, pianist and composer. Commonly nicknamed the "Rocket Man" after his 1972 hit single of the same name, John has led a commercially successful career a ...
was criticized for touring Russia in 1979, he responded: "I wouldn't say I won't tour in America because I can't stand Anita Bryant". In his song " Mañana", Jimmy Buffett sings "I hope Anita Bryant never ever does one of my songs". In 1978, David Allan Coe
David Allan Coe (born September 6, 1939) is an American singer and songwriter. Coe took up music after spending much of his early life in reform schools and prisons, and first became notable for busking in Nashville. He initially played mostly i ...
recorded the song "Fuck Aneta Briant" on his album '' Nothing Sacred''. California punk rock band Dead Kennedys
Dead Kennedys are an American punk rock band that formed in San Francisco, California, in 1978. The band was one of the defining punk rock, punk bands during its initial eight-year run.
Dead Kennedys' lyrics were usually political in nature, sa ...
referenced Bryant in their song "Moral Majority" from their 1981 EP '' In God We Trust, Inc.''
In 1977, the Dutch ''levenslied Levenslied (Dutch, literally "life song" or "song about life") is a sentimental Dutch-language subgenre of popular music. ''Levenslied'' lyrics can be sweet or bitter, light and sentimental, but also reflective and dark, about subjects such as love, ...
'' singer Zangeres Zonder Naam
Maria (Mary) Servaes-Beij (; Leiden, 5 August 1919 – Horn, Netherlands, 23 October 1998) was a Dutch levenslied singer. She performed under the stage name Zangeres Zonder Naam (English: Singer without a name). She recorded almost 600 songs over ...
wrote the protest song "Luister Anita" ("Listen Up, Anita") on the occasion of the protest night "Miami Nightmare", organized in the Amsterdam Concertgebouw
The Royal Concertgebouw ( nl, Koninklijk Concertgebouw, ) is a concert hall in Amsterdam, Netherlands. The Dutch term "concertgebouw" translates into English as "concert building". Its superb acoustics place it among the finest concert halls in ...
. The nightly concert was intended to raise funds for an advertisement in ''Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to ...
'', in which the Dutch nation was to call on the American people to protect the rights of minorities. In the song, Zangeres Zonder Naam compared Anita Bryant to Hitler and called on homosexuals to fight for their rights. The song became an integral part of her repertoire and cemented her status as a cult figure among Dutch homosexuals.
Steve Gerber
Stephen Ross Gerber (; September 20, 1947 – February 10, 2008) was an American comic book writer and creator of the satiric Marvel Comics character Howard the Duck. Other works include '' Man-Thing'', '' Omega the Unknown,'' '' Marvel Spotlig ...
, in his ''Howard the Duck
Howard the Duck is a fictional Character (arts), character appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. The character was created by writer Steve Gerber and artist Val Mayerik. Howard the Duck first appeared in ''Adventure into F ...
'' for Marvel Comics
Marvel Comics is an American comic book publishing, publisher and the flagship property of Marvel Entertainment, a divsion of The Walt Disney Company since September 1, 2009. Evolving from Timely Comics in 1939, ''Magazine Management/Atlas Co ...
, made an organization called the Sinister S.O.O.F.I. (Save Our Offspring from Indecency) who were led by Anita Bryant. Although it was not explicitly stated, even ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' called the implication "transparent".
Bryant was regularly lampooned on ''Saturday Night Live
''Saturday Night Live'' (often abbreviated to ''SNL'') is an American late-night live television sketch comedy and variety show created by Lorne Michaels and developed by Dick Ebersol that airs on NBC and Peacock. Michaels currently serves a ...
'', sometimes with her politics as the target, sometimes her reputation as a popular, traditional entertainer known for her commercials as the target, and sometimes targeting a combination of the two. Her name was also a frequent punchline on ''The Gong Show
''The Gong Show'' is an American amateur talent contest franchised by Sony Pictures Television to many countries. It was broadcast on NBC's daytime schedule from June 14, 1976, through July 21, 1978, and in first-run syndication from 1976 to 1 ...
'', such as the time host/producer Chuck Barris
Charles Hirsch Barris (June 3, 1929 – March 21, 2017) was an American game show creator, producer, and host. Barris was known for hosting ''The Gong Show'' and creating ''The Dating Game'' and ''The Newlywed Game''. He was also a songwrite ...
joked that Bryant was releasing a new Christmas album called ''Gay Tidings''. Some references were less overtly political, but equally critical. In the film ''Airplane!
''Airplane!'' (alternatively titled ''Flying High!'') is a 1980 American parody film written and directed by the brothers David Zucker, David and Jerry Zucker, and Jim Abrahams in their directorial debuts, and produced by Jon Davison (film prod ...
'', Leslie Nielsen
Leslie William Nielsen (11 February 192628 November 2010) was a Canadian actor and comedian. With a career spanning 60 years, he appeared in more than 100 films and 150 television programs, portraying more than 220 characters.
Nielsen was bo ...
's character, upon seeing a large number of passengers become violently ill, vomit, and have uncontrollable flatulence, remarked: "I haven't seen anything like this since the Anita Bryant concert." Other television shows that targeted her were ''Soap'', ''Designing Women
''Designing Women'' is an American television sitcom created by Linda Bloodworth-Thomason that aired on CBS from September 29, 1986, to May 24, 1993, producing seven seasons and 163 episodes. It was a joint production of Bloodworth/Thomason ...
'', and ''The Golden Girls
''The Golden Girls'' is an American sitcom created by Susan Harris that aired on NBC from September 14, 1985, to May 9, 1992, with a total of 180 half-hour episodes, spanning seven seasons. With an ensemble cast starring Bea Arthur, Betty White ...
''. She was also the target of mockery in the RiffTrax
RiffTrax is an American company that produces scripted humorous commentary tracks which are synced to mostly public domain feature films, education shorts, and television episodes. With the talents of former ''Mystery Science Theater 3000'' (''M ...
short ''Drugs Are Like That''.
Armistead Maupin
Armistead Jones Maupin, Jr. ( ) (born May 13, 1944) is an American writer notable for '' Tales of the City'', a series of novels set in San Francisco.
Early life
Maupin was born in Washington, D.C., to Diana Jane (Barton) and Armistead Jones Ma ...
, in his 1980 novel '' More Tales of the City'', used Anita Bryant's "Save Our Children" campaign to prompt a principal character to come out
Coming out of the closet, often shortened to coming out, is a metaphor used to describe LGBT people's self-disclosure of their sexual orientation, romantic orientation, or gender identity.
Framed and debated as a privacy issue, coming out of ...
of the closet
''Closeted'' and ''in the closet'' are metaphors for lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender and other (LGBTQ+) people who have not disclosed their sexual orientation or gender identity and aspects thereof, including sexual identity and human ...
.
In the cold open
A cold open (also called a teaser sequence) is a narrative technique used in television and films. It is the practice of jumping directly into a story at the beginning of the show before the title sequence or opening credits are shown. In Ameri ...
of a 2005 episode of ''Will and Grace
Will may refer to:
Common meanings
* Will and testament, instructions for the disposition of one's property after death
* Will (philosophy), or willpower
* Will (sociology)
* Will, volition (psychology)
* Will, a modal verb - see Shall and wi ...
'', 'Dance Cards and Greeting Cards', Karen Walker refers to Bryant as her former arch nemesis and references Bryant's former position as the spokesman for the Florida Citrus Commission: "Well, I said the same thing to him I said to Anita: "Squeeze your own oranges!"".
Bryant appears in archive footage as a principal antagonist in the 2008 American biographical film ''Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. Immune factors and immune ...
,'' about the life of gay rights activist and politician Harvey Milk
Harvey Bernard Milk (May 22, 1930 – November 27, 1978) was an American politician and the first openly gay man to be elected to public office in California, as a member of the San Francisco Board of Supervisors. Milk was born and raised in ...
. She was also portrayed as the principal antagonist in the 2011 play, ''Anita Bryant Died For Your Sins.''
In May 2013, producers announced plans for a biographical HBO
Home Box Office (HBO) is an American premium television network, which is the flagship property of namesake parent subsidiary Home Box Office, Inc., itself a unit owned by Warner Bros. Discovery. The overall Home Box Office business unit is ba ...
film based on Bryant's life to star Uma Thurman
Uma Karuna Thurman (born April 29, 1970) is an American actress and former model. She has performed in a variety of films, from romantic comedies and dramas to science fiction and action films. Following her appearances on the December 1985 an ...
, with a script from gay screenwriter Chad Hodge
Chad Hodge (born 1977) is an American writer and producer who created drama series '' Runaway'' (2006), '' The Playboy Club'' (2011), '' Wayward Pines'' (2015), and '' Good Behavior'' (2016). He wrote the Broadway stage adaptation of Irving Berlin ...
. Long languishing in development, as of 2019, Ashley Judd
Ashley Judd (born Ashley Tyler Ciminella; April 19, 1968) is an American actress. She grew up in a family of performing artists: she is the daughter of the late country music singer Naomi Judd and the half-sister of country music singer Wynonna ...
and Neil Patrick Harris
Neil Patrick Harris (born June 15, 1973) is an American actor, singer, writer, producer, and television host. Primarily known for his comedic television roles and dramatic and musical stage roles, he has received multiple accolades throughout ...
have been attached to the project.
Bryant's likeness is portrayed by a drag performer in the comedic play, ''Anita Bryant's Playboy Interview,'' which premiered in 2016 in Silver Lake, Los Angeles
Silver Lake is a residential and commercial Neighbourhood, neighborhood in the east-Central Los Angeles, central region of Los Angeles, California. Originally home to a small community called Ivanhoe in honor of Walter Scott, Sir Walter Scott. In ...
and is based on her 1978 ''Playboy
''Playboy'' is an American men's lifestyle and entertainment magazine, formerly in print and currently online. It was founded in Chicago in 1953, by Hugh Hefner and his associates, and funded in part by a $1,000 loan from Hefner's mother.
K ...
'' interview with Ken Kelley. Bryant is a frequently portrayed character at drag shows across the United States.
Bryant is the subject of the musical ''The Loneliest Girl in the World,'' which had its world premiere run at Diversionary Theatre in San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the List of United States cities by population, eigh ...
during mid-2018.
Archive footage
Stock footage, and similarly, archive footage, library pictures, and file footage is film or video footage that can be used again in other films. Stock footage is beneficial to filmmakers as it saves shooting new material. A single piece of stock ...
of her was used in '' The Gospel of Eureka'', a 2018 documentary by Michael Palmieri and Donal Mosher about the lives of LGBT individuals and evangelical Christians in Eureka Springs, Arkansas
Eureka Springs is a city in Carroll County, Arkansas, United States, and one of two county seats for the county. It is located in the Ozark Mountains of northwest Arkansas, near the border with Missouri. As of the 2020 census, the city populati ...
.
See also
* Anti-LGBT slogans *Homophobic propaganda
Homophobic propaganda (or anti-gay propaganda) is propaganda based on homonegativity and homophobia towards homosexual and sometimes other non-heterosexual people. Such propaganda supports anti-gay prejudices and stereotypes, and promotes socia ...
References
External links
Anita Bryant Ministries International
*
Image of Anita Bryant in the 1970s
(Available for public use from the
State Archives of Florida
The State Library and Archives of Florida is the central repository for the archives of state government for the state of Florida. It is located at the R.A. Gray Building on 500 South Bronough Street in Tallahassee, Florida, Florida's capital.
M ...
)Belated curtain call
''Tulsa World'', April 19, 2007
Readers Forum: Anita Bryant to star in Round-Up 2007
''Tulsa World'', April 18, 2007
Celebration draws Anita Bryant back to Barnsdall
''Tulsa World'', May 28, 2005
''
Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture
The Oklahoma Historical Society (OHS) is an agency of the government of Oklahoma dedicated to promotion and preservation of Oklahoma's history and its people by collecting, interpreting, and disseminating knowledge and artifacts of Oklahoma. ...
''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bryant, Anita
1940 births
Living people
20th-century American singers
20th-century American women singers
21st-century American women
Activists from Florida
Activists from Oklahoma
American gospel singers
American political activists
American women activists
American women pop singers
Baptists from Oklahoma
Carlton Records artists
Columbia Records artists
Conservatism in the United States
Discrimination against LGBT people in the United States
LGBT history in Florida
Miss America 1950s delegates
Musicians from Tulsa, Oklahoma
People from Osage County, Oklahoma
Singers from Oklahoma
Southern Baptists
Traditional pop music singers
Women in Florida politics
Word Records artists
Anti-LGBT sentiment
USO Entertainer